
The UK government is making major changes to its R&D tax credit system from April 2024 onwards. These reforms have the stated intent of making the process easier, fairer, and targeting resources at companies that genuinely conduct research and development. The two major updates are the Merged Scheme and the Enhanced R&D Intensive Scheme (ERIS). Here’s what businesses need to know.
The Merged Scheme
Previously, there were two main R&D tax relief schemes: the SME R&D Relief for smaller businesses and the RDEC (Research and Development Expenditure Credit) for larger ones. From April 2024, these will combine into a single scheme applicable to all businesses, regardless of size. The merged scheme has several implications:
- Uniform Tax Relief Rates:
- Profitable companies will receive effective relief at 15p for every £1 spent on qualifying R&D if taxed at the main 25% rate or 16.2p if taxed at the 19% small profits rate.
- Loss-making companies can claim 16.2p per £1 of qualifying spend.
- Qualifying R&D Costs:
- The scheme aligns with RDEC rules but allows broader subcontractor claims. For instance, all companies can claim subcontracted R&D costs, provided they were expected to involve R&D efforts when contracts were made.
- Taxable Credit:
- The relief will appear as taxable income in company accounts, maintaining consistency with existing RDEC rules.
While this simplification reduces disparities between company sizes, SMEs that previously benefited from higher relief rates under the SME scheme may see reduced benefits unless they qualify for ERIS.
The Enhanced R&D Intensive Scheme (ERIS)
ERIS supports small and medium enterprises (SMEs) heavily involved in R&D. To qualify, at least 40% of total business expenditure must relate to qualifying R&D activities (30% after 1st April 2024). Key features include:
- Higher Relief for Loss-Making Companies:
- Eligible businesses can claim a payable tax credit of up to 14.5% of their enhanced loss, which is calculated by adding an 86% uplift to R&D expenditure.
- For example, a company with £100,000 in qualifying R&D could generate an adjusted loss of £186,000, resulting in a credit worth £26,970.
- Targeted Support:
- ERIS is particularly beneficial for companies investing heavily in innovative activities but not yet generating profits.
The transition period
During the transition period to the new schemes, there are five R&D schemes available at once! Navigating this landscape can be tricky, and Kapitalise is here to help.
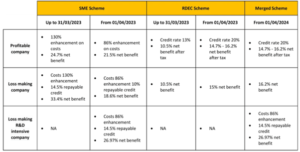
The different schemes and rates of return are summarised below:
*Loss-making R&D intensive companies are those whose qualifying R&D expenditure constitutes at least 40% (for costs from 1st April 2023) or 30% (for accounting periods from 1st April 2024) of total expenditure (splitting accounting periods as required).
Practical Considerations for Businesses
- Advance Notifications: Since April 2023, companies new to R&D claims or with significant claim gaps must notify HMRC within six months of their accounting period.
- Additional Information Forms: From August 2023, claims must include detailed forms to ensure compliance and reduce fraud.
These procedural updates ensure that only legitimate R&D activities qualify, reflecting HMRC’s stricter scrutiny.
The Impact on Businesses
While the merged scheme streamlines the tax credit system, its uniformity means some companies might see reduced benefits, and some will see increased benefits. As these changes roll out, companies should review their R&D strategies.
Kapitalise helps your business navigate the process from start to finish. We represent your business with HMRC even after you receive your tax relief. To find out how we can help you, please contact us.